第24节 ETCD
❤️💕💕新时代拥抱云原生,云原生具有环境统一、按需付费、即开即用、稳定性强特点。Myblog:http://nsddd.top
[TOC]
ETCD 介绍
etcd address
etcd (aid) 是分布式系统最关键数据的分布式可靠键值存储,重点是:
- 简单:定义明确、面向用户的 API (gRPC)
- 安全:具有可选客户端证书身份验证的自动 TLS
- 快速:基准测试 10,000 次写入/秒
- 可靠:使用 Raft 正确分布
etcd是一种高度一致的分布式键值存储,它提供了一种可靠的方式来存储需要由分布式系统或机器集群访问的数据。它在网络分区期间优雅地处理领导选举,并且可以容忍机器故障,即使在
leader node中也是如此。
不管是 kubernetes 的深入学习中,遇到了很多关于 etcd 的知识,又或者是本身关于 k3s runtime 支持,关于 etcd 作为内嵌 DB 也遇到了很多疑惑,所以有了这篇。
etcd 是用 Go 编写的,使用Raft共识算法来管理一个高可用的复制日志。
提醒
etcd 是一款分布式存储的中间件,使用 Go语言 编写并通过 Raft 一致性算法处理和确保分布式一致性。解决数据一致性问题,用于微服务架构中的服务注册与发现中心。
一些关于 Raft 的问题,我想在下一篇你能找到答案
如果你需要看到关于 etcd - raft 算法的 Go语言 实现。
是不是可以理解我们之前无论是部署 hedoop 还是 kubernetes ,都是存在一个问题:尽量选择奇数的节点,真是因为 raft。
分布式 CAP 理论
提示
consistency(一致性)、Availability(可用性)、Partition tolerance(分区容错性)
这三个特性只能同时实现两点,不能三点同时兼顾~
分布式系统的基本特性:Partition tolerance(分区容错性) 必须要满足
consistency(一致性)、Availability(可用性) 二选一:
- 银行选择数据一致性
- 大众网页选择服务可用性
etcd 归根结底是一个存储组件,可以实现配置共享和服务发现~
etcd 常用术语
| 术语 | 描述 | 备注 |
|---|---|---|
| Raft | Raft算法,etcd实现一致性的核心 | etcd有etcd-raft模块 |
| Follower | Raft中的从属节点 | 竞争Leader失败 |
| Leader | Raft中的领导协调节点,用于处理数据提交 | Leader节点协调整个集群 |
| Candidate | 候选节点 | 当Follower接收Leader节点的消息超时会转变为candidate |
| Node | Raft状态机的实例 | Raft中设计多个节点 |
| Member | etcd实例,管理对应的Node节点 | 可处理客户端请求 |
| Peer | 同一个集群中的另一个Member | 其他成员 |
| Cluster | etcd集群 | 拥有多个etcd memeber |
| Lease | 租期 | 关键设置的租期,过期删除 |
| Watch | 检测机制 | 监控简直对的变化 |
| Term | 任期 | 某个节点成为Leader,到下一次竞选的事件 |
| WAL | 预写式日志 | 用于持久化存储的日志格式 |
| client | 客户端 | 向etcd发起请求的客户端 |
注意
在分布式系统和 kubernetes 集群中,etcd 可以作为服务注册与发现和键值对存储组件。
- 键值对存储:etcd 是一个用于键值对的存储,kubernetes 元数据存储
- 服务注册与发现:raft 算法保证分布式场景一致性。
- 消息订阅与发现
- 分布式锁:基于 raft 算法,很容易实现
架构
搭建 etcd
可以使用:
yum install etcd
yaml 安装的二进制文件:
名称 位置 etcd /usr/bin/etcd etcdctl /usr/bin/etcdctl etcd.service /lib/systemd/system/etcd.service etcd.conf /etc/etcd/etcd.conf
推荐使用 二进制 、 源码编译、docker安装:
高可用安装 – 避免单点故障
启动方式
- 静态启动
- etcd 动态发现
- DNS 发现
goreman 是一个 Go语言 编写的多进程管理工具,是对 ruby 下广泛使用的 Foreman 的重写~
go get github.com/mattn/goreman
安装:
go install github.com/mattn/goreman@latest
使用goreman 启动 etcd 集群
goreman -f /opt/procfile start
docker部署
提示
个人比较倾向于这种方式,个人电脑配置不行~
构建思路
| 节点名 | IP地址 |
|---|---|
| node1 | 10.2.36.1 |
| node2 | 10.2.36.2 |
| node3 | 10.2.36.3 |
我们需要三个节点,这三个节点可以分布在不同服务器,本案例中,以一台服务器基于Docker运行多个容器来做演示。
下载Etcd镜像
root@ubuntu:~# docker pull quay.io/coreos/etcd
root@ubuntu:~# docker images | grep "etcd"
quay.io/coreos/etcd latest 61ad63875109 4 years ago 39.5MB
创建自定义Docker网络
docker 基础篇 我们知道啦docker网络模式,我们选择自定义网络。
首先构建个自定义网络,因为我们要给各个节点分配IP地址,Docker容器默认网络只能自动配IP无法手动分配。
⚠️ 注意:即使是自定义网络,我选择的也是默认的网桥模式(创建一个新的bridge网络)
--driver:驱动程序类型--subnet:代表网段的CIDR格式的子网--gateway:主子网的IPV4和IPV6的网关mynet2:是自定义网络名称
root@ubuntu:~# docker network create --driver bridge --subnet=10.2.36.0/16 --gateway=10.2.1.1 mynet2
be11fe7f1fc8ea9fe30e018297295b8c61a823bb31f647aa4da777fa3eee63a7
root@ubuntu:~# docker network ls |grep "mynet2"
be11fe7f1fc8 mynet2 bridge local
创建并启动Etcd镜像节点
参数📜 对下面的解释
如图表:
节点 1 🔽
docker run -d \
-p 2479:2379 \
-p 2381:2380 \
--name node1 \
--network=mynet2 \
--ip 10.2.36.1 \
quay.io/coreos/etcd:latest \
etcd \
-name node1 \
-advertise-client-urls http://10.2.36.1:2379 \
-initial-advertise-peer-urls http://10.2.36.1:2380 \
-listen-client-urls http://0.0.0.0:2379 -listen-peer-urls http://0.0.0.0:2380 \
-initial-cluster-token etcd-cluster \
-initial-cluster "node1=http://10.2.36.1:2380,node2=http://10.2.36.2:2380,node3=http://10.2.36.3:2380" \
-initial-cluster-state new
节点 2 🔽
docker run -d \
-p 2579:2379 \
-p 2382:2380 \
--name node2 \
--network=mynet2 \
--ip 10.2.36.2 \
quay.io/coreos/etcd:latest \
etcd \
-name node2 \
-advertise-client-urls http://10.2.36.2:2379 \
-initial-advertise-peer-urls http://10.2.36.2:2380 \
-listen-client-urls http://0.0.0.0:2379 -listen-peer-urls http://0.0.0.0:2380 \
-initial-cluster-token etcd-cluster \
-initial-cluster "node1=http://10.2.36.1:2380,node2=http://10.2.36.2:2380,node3=http://10.2.36.3:2380" \
-initial-cluster-state new
节点 3 🔽
docker run -d \
-p 2679:2379 \
-p 2383:2380 \
--name node3 \
--network=mynet2 \
--ip 10.2.36.3 \
quay.io/coreos/etcd:latest \
etcd \
-name node3 \
-advertise-client-urls http://10.2.36.3:2379 \
-initial-advertise-peer-urls http://10.2.36.3:2380 \
-listen-client-urls http://0.0.0.0:2379 -listen-peer-urls http://0.0.0.0:2380 \
-initial-cluster-token etcd-cluster \
-initial-cluster "node1=http://10.2.36.1:2380,node2=http://10.2.36.2:2380,node3=http://10.2.36.3:2380" \
-initial-cluster-state new
verification
root@ubuntu:~# docker ps | grep "node"
2986d95eedd4 quay.io/coreos/etcd:latest "etcd -name node3 -a…" 50 seconds ago Up 49 seconds 0.0.0.0:2679->2379/tcp, :::2679->2379/tcp, 0.0
93e41bb72642 quay.io/coreos/etcd:latest "etcd -name node2 -a…" 54 seconds ago Up 53 seconds 0.0.0.0:2579->2379/tcp, :::2579->2379/tcp, 0.0
bae0df00930c quay.io/coreos/etcd:latest "etcd -name node1 -a…" About a minute ago Up 59 seconds 0.0.0.0:2479->2379/tcp, :::2479->2379/tcp, 0.0
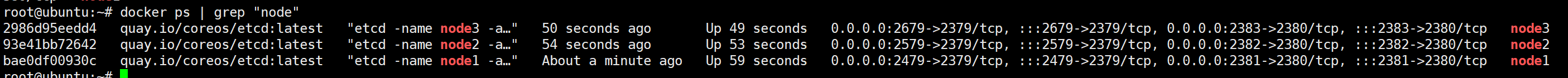
succeed
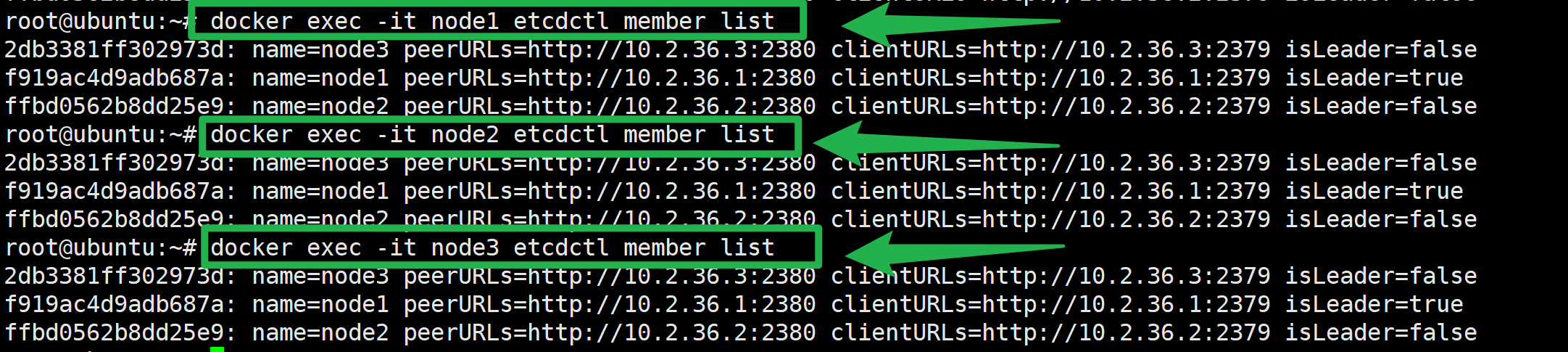
通过etcdctl member list命令可以查询出所有集群节点的列表即为成功
docker exec -it node1 etcdctl member list
docker exec -it node2 etcdctl member list
docker exec -it node3 etcdctl member list
自定义网络本身就维护好了主机名和ip的对应关系(ip和域名都能通)
动态发现启动 etcd
etcd 操作
基于 etcd 自带的客户端工具 – etcdctl 来进行一些列操作,同样的 v2 和 v3 的版本也是不一样会的
提示
etcdctl 是一个命令行,便于我们进行服务测试或者手动修改数据
export ETCDCTL_API=2
export ETCDCTL_API=3
查询:
root@ubuntu:/c# docker exec -it node2 etcdctl -v
etcdctl version: 3.3.8
API version: 2
常用命令
提示
常用命令分为 数据库操作 和 非数据库操作 两种类型。
帮助信息:
etcdctl -h
etcd 在键的组织上采用了层次化的空间结构(类似于文件系统中目录的概念),数据库操作围绕对键值和目录的 CRUD [增删改查](符合 REST 风格的一套操作:Create, Read, Update, Delete)完整生命周期的管理。
查看集群状态:
ETCDCTL_API=3 etcdctl endpoint status --cluster -w table
常用命令:
# 列表
etcdctl ls /kube-centos/network/config
# 查看
etcdctl get /kube-centos/network/config
# v2移除
etcdctl rm /kube-centos/network/config
# v3移除
ETCDCTL_API=3 etcdctl del /kube-centos/network/config
# 递归移除
etcdctl rm --recursive registry
# 修改
etcdctl mk /kube-centos/network/config "{ \"Network\": \"172.30.0.0/16\", \"Backend\": { \"Type\": \"vxlan\" } }"
# 命令将数据存到指定位置。这部分数据可以用来灾难恢复
etcdctl backup
# 健康检查
etcdctl endpoint health
命令合集:
#存储:
curl http://127.0.0.1:4001/v2/keys/testkey -XPUT -d value='testvalue'
curl -s http://127.0.0.1:4001/v2/keys/message2 -XPUT -d value='hello etcd' -d ttl=5
#获取:
curl http://127.0.0.1:4001/v2/keys/testkey
#查看版本:
curl http://127.0.0.1:4001/version
#删除:
curl -s http://127.0.0.1:4001/v2/keys/testkey -XDELETE
#监视:
窗口1:curl -s http://127.0.0.1:4001/v2/keys/message2 -XPUT -d value='hello etcd 1'
curl -s http://127.0.0.1:4001/v2/keys/message2?wait=true
窗口2:
curl -s http://127.0.0.1:4001/v2/keys/message2 -XPUT -d value='hello etcd 2'
自动创建key:
curl -s http://127.0.0.1:4001/v2/keys/message3 -XPOST -d value='hello etcd 1'
curl -s 'http://127.0.0.1:4001/v2/keys/message3?recursive=true&sorted=true'
#创建目录:
curl -s http://127.0.0.1:4001/v2/keys/message8 -XPUT -d dir=true
#删除目录:
curl -s 'http://127.0.0.1:4001/v2/keys/message7?dir=true' -XDELETE
curl -s 'http://127.0.0.1:4001/v2/keys/message7?recursive=true' -XDELETE
#查看所有key:
curl -s http://127.0.0.1:4001/v2/keys/?recursive=true
#存储数据:
curl -s http://127.0.0.1:4001/v2/keys/file -XPUT --data-urlencode value@upfile
#使用etcdctl客户端:
#存储:
etcdctl set /liuyiling/testkey "610" --ttl '100'
--swap-with-value value
#获取:
etcdctl get /liuyiling/testkey
#更新:
etcdctl update /liuyiling/testkey "world" --ttl '100'
#删除:
etcdctl rm /liuyiling/testkey
#使用ca获取:
etcdctl --cert-file=/etc/etcd/ssl/etcd.pem --key-file=/etc/etcd/ssl/etcd-key.pem --ca-file=/etc/etcd/ssl/ca.pem get /message
#目录管理:
etcdctl mk /liuyiling/testkey "hello" 类似set,但是如果key已经存在,报错
etcdctl mkdir /liuyiling
etcdctl setdir /liuyiling
etcdctl updatedir /liuyiling
etcdctl rmdir /liuyiling
#查看:
etcdctl ls --recursive
#监视:
etcdctl watch mykey --forever + etcdctl update mykey "hehe"
#监视目录下所有节点的改变
etcdctl exec-watch --recursive /foo -- sh -c "echo hi"
etcdctl exec-watch mykey -- sh -c 'ls -al' + etcdctl update mykey "hehe"
etcdctl member list
对象为键值
set[增:无论是否存在]:
etcdctl set key valuemk[增:必须不存在]:
etcdctl mk key valuerm[删]:
etcdctl rm keyupdate[改]:
etcdctl update key valueget[查]:
etcdctl get key
对象为目录
setdir[增:无论是否存在]:
etcdctl setdir dirmkdir[增:必须不存在]:
etcdctl mkdir dirrmdir[删]:
etcdctl rmdir dirupdatedir[改]:
etcdctl updatedir dirls[查]:
etcdclt ls
非数据库操作命令
backup[备份 etcd 的数据]
etcdctl backupwatch[监测一个键值的变化,一旦键值发生更新,就会输出最新的值并退出]
etcdctl watch keyexec-watch[监测一个键值的变化,一旦键值发生更新,就执行给定命令]
etcdctl exec-watch key --sh -c "ls"member[通过 list、add、remove、update 命令列出、添加、删除 、更新etcd 实例到 etcd 集群中]
etcdctl member list;etcdctl member add 实例;etcdctl member remove 实例;etcdctl member update 实例。etcdctl cluster-health[检查集群健康状态]
常用配置参数
设置配置文件,默认为/etc/etcd/etcd.conf。
| 配置参数 | 参数说明 |
|---|---|
| 配置参数 | 参数说明 |
| -name | 节点名称 |
| -data-dir | 保存日志和快照的目录,默认为当前工作目录,指定节点的数据存储目录 |
| -addr | 公布的ip地址和端口。 默认为127.0.0.1:2379 |
| -bind-addr | 用于客户端连接的监听地址,默认为-addr配置 |
| -peers | 集群成员逗号分隔的列表,例如 127.0.0.1:2380,127.0.0.1:2381 |
| -peer-addr | 集群服务通讯的公布的IP地址,默认为 127.0.0.1:2380. |
| -peer-bind-addr | 集群服务通讯的监听地址,默认为-peer-addr配置 |
| -wal-dir | 指定节点的was文件的存储目录,若指定了该参数,wal文件会和其他数据文件分开存储 |
| -listen-client-urls | |
| -listen-peer-urls | 监听URL,用于与其他节点通讯 |
| -initial-advertise-peer-urls | 告知集群其他节点url. |
| -advertise-client-urls | 告知客户端url, 也就是服务的url |
| -initial-cluster-token | 集群的ID |
| -initial-cluster | 集群中所有节点 |
| -initial-cluster-state | -initial-cluster-state=new 表示从无到有搭建etcd集群 |
| -discovery-srv | 用于DNS动态服务发现,指定DNS SRV域名 |
| -discovery | 用于etcd动态发现,指定etcd发现服务的URL [https://discovery.etcd.io/],用环境变量表示 |
Go 和 etcd 交互
package main
import (
"context"
"log"
"time"
"go.etcd.io/etcd/client/v3"
)
func main() {
cli, err := clientv3.New(clientv3.Config{
Endpoints: []string{"http://10.2.36.1:2479", "http://10.2.36.2:2579", "http://10.2.36.3:2679"},
DialTimeout: 5 * time.Second,
})
if err != nil {
panic(err)
}
defer cli.Close()
testKey := "/test/key" //设置 key
testValue := "I love docker" //设置 value
_, err = cli.Put(context.Background(), testKey, testValue)
if err != nil {
log.Fatal("Put failed:", err)
}
res, err := cli.Get(context.Background(), testKey)
if err != nil {
log.Fatal("Get failed:", err)
}
kvs := res.Kvs
val := string(kvs[0].Value)
log.Println("result:", val == testValue)
}
gPRC 代理模式
gPRC 代理模式 – 实现可伸缩的 etcd API
gRPC proxy 是在 gRPC 层 运行的无状态 etcd 反向代理
旨在减少 etcd 集群上的总处理负载
END 链接
✴️版权声明 © :本书所有内容遵循CC-BY-SA 3.0协议(署名-相同方式共享)©